Indoor Residual Spraying
IRS

History of IRS
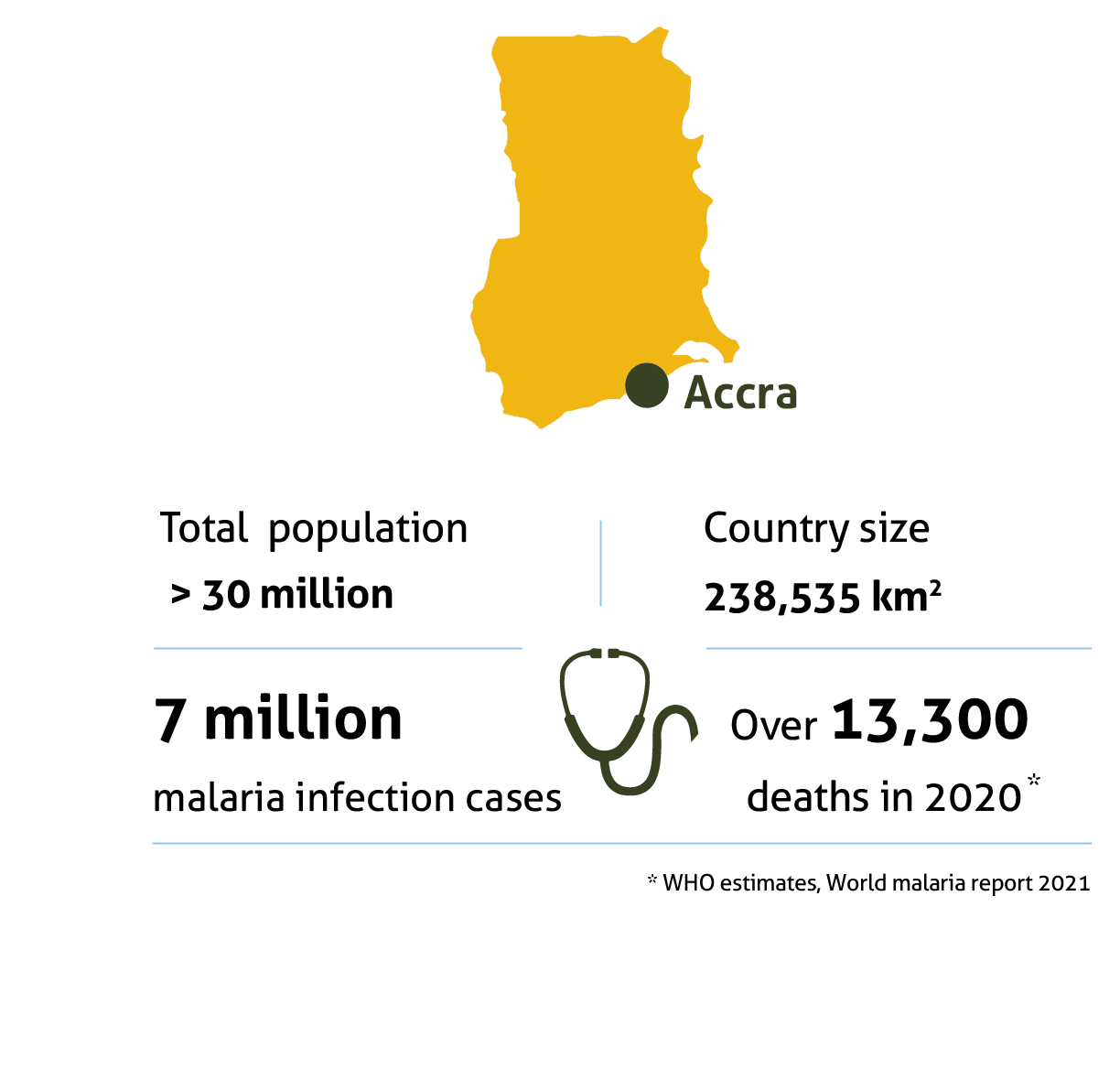
The IRS Campaign
Historical Perspectives
The Pre-Operational Activities include
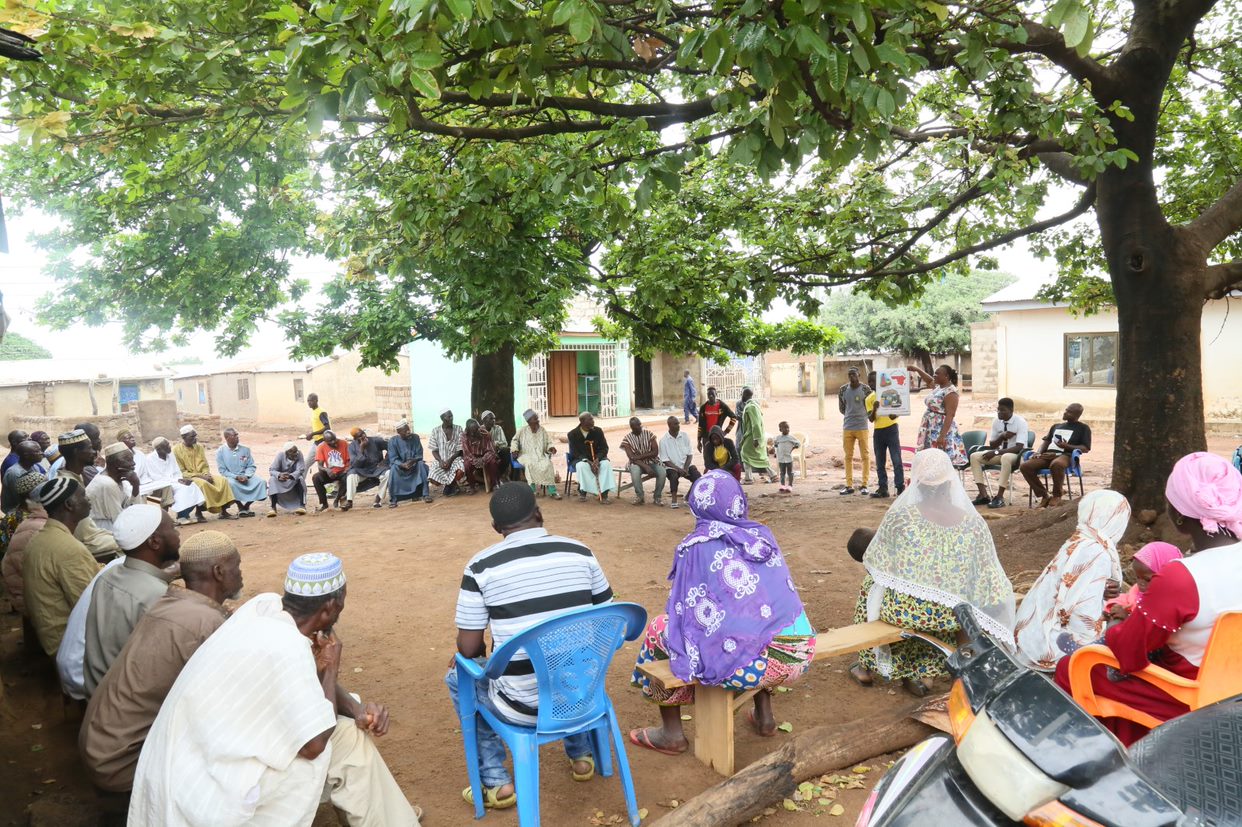
Community entry in new and already existing communities
With the benefit of already documented information about the community, key opinion leaders/influential people are identified and their support is sought for successful program implementation. These include the traditional authorities, religious leaders, heads of regulatory and partnering institutions, the District Chief Executive, and heads of other institutions.
Recruitment & capacity building for staff
There is training for the entire operational staff. The recruits get a longer training period than staff who were engaged in the previous season. While these pieces of training are going on, the SBCC team starts with targeted SBCC in communities that recorded a lot of refusals from previous spray season’s records.
Media Campaign To Support Spraying Initiative
The contracted stations transmit jingles, announcements and do Live Presenter Mentions (LPM) daily and hold weekly panel discussions to educate the communities and get the necessary feedback for program improvement. Community announcements (gong-gong beating, mosques & churches) mass announcements (using Public Address systems fixed on vehicles) are also used at the community level for information dissemination and education.
Data Management
This department is primarily responsible for collecting, validating, processing and storing all IRS and related data in manner that is reliable, accessible and timely to facilitate effective decision making and track progress towards program objectives.
Entomology
The Entomology provides data on vector transmission dynamics, insecticide resistance profiles, insecticide batch potencies, effectiveness of spray applications, efficacy of insecticides used for the IRS operations on sprayed surfaces and the elucidation of mechanisms of insecticide resistance and its impact on the vector control.

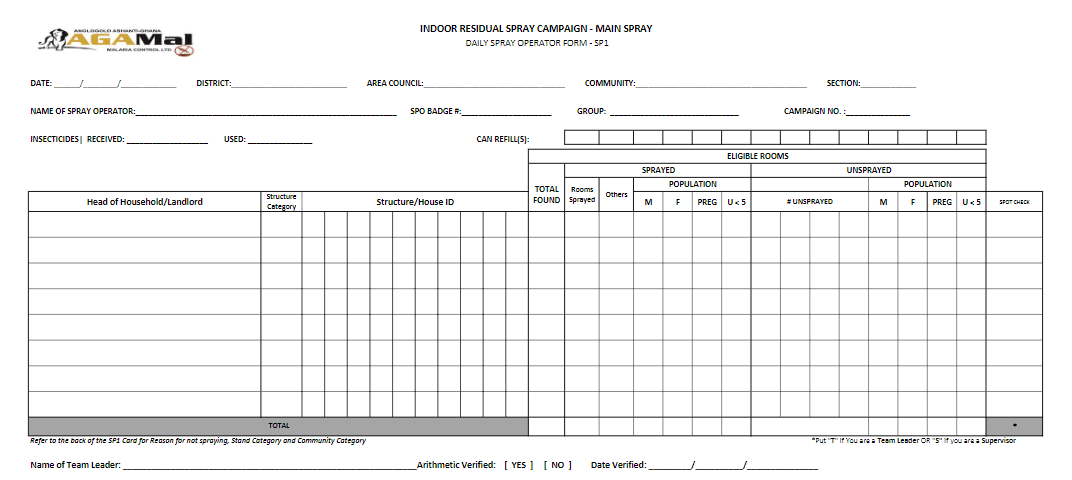
The house to house mobilization / sensitization and spraying. The actual spraying of communities occurs in this phase. At the end of the training of spray operators, the spray teams move from house to house in the communities to spray. The SBCC teams adequately prepare householders. The spray operator on reaching the house introduces himself with the Identification Card. With the permission of the householder, the spray operator together with the householder enters to inspect the rooms to be sprayed which are usually prepared as directed by the SBCC team. The operator then comes out to mix his insecticide, explaining every step to the householder after which he asks the householder to stay at a safe distance for spraying to be done in the rooms. Afterward, the spray operator reminds the householder to stay outside for a minimum of two hours. Household data, as recorded on the SP1 card, is submitted to the team leader who in turn collates and submits to the group supervisor. At the end of the day’s work, the spray operator returns to sprayed houses and does the final inspection of rooms to ensure the householder is satisfied with work done. The householder then signs the card. Communities earmarked for IRS are appropriately entered and prepared for at least three (3) days before spraying takes place.
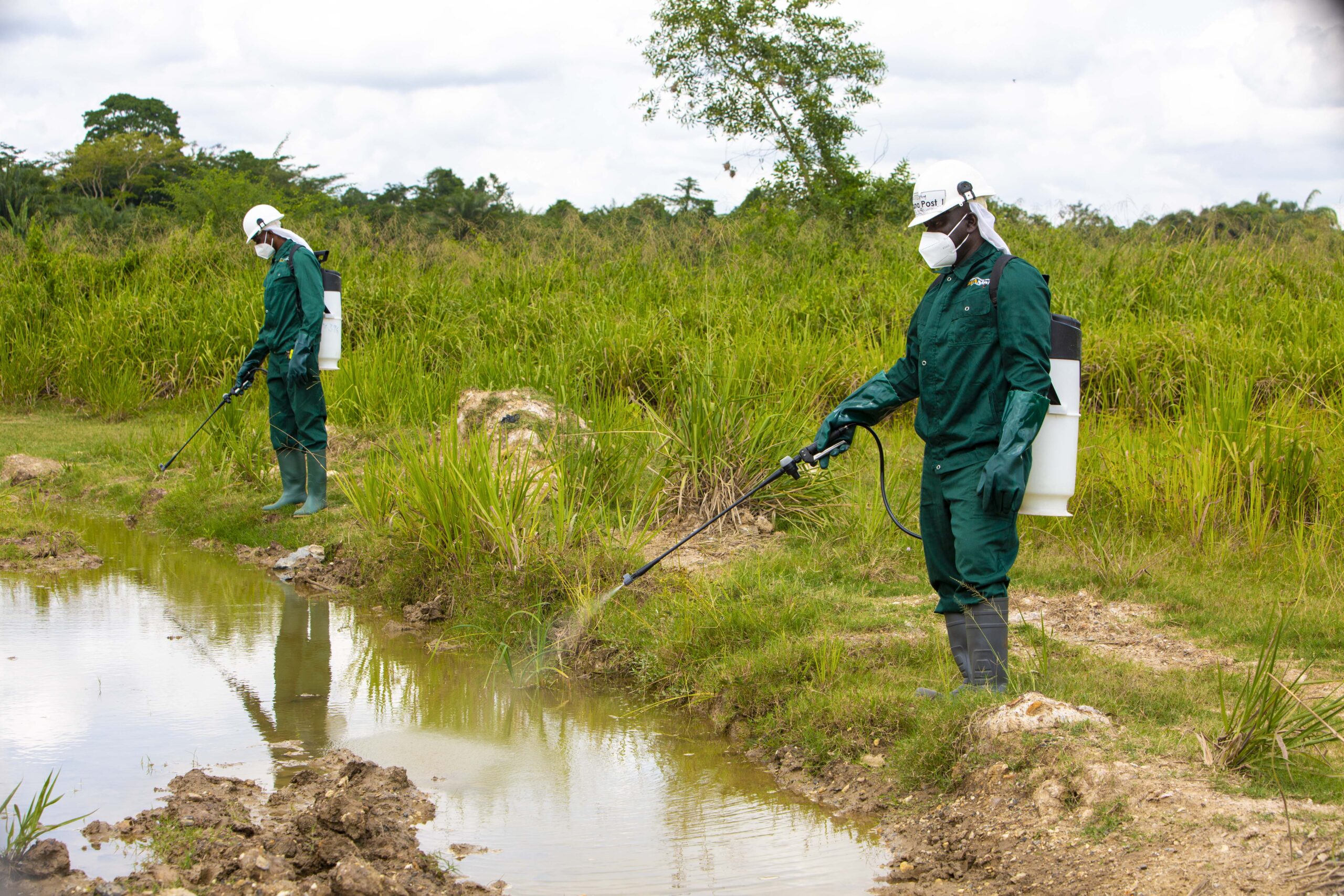


The house to house mobilization / sensitization and spraying. The actual spraying of communities occurs in this phase. At the end of the training of spray operators, the spray teams move from house to house in the communities to spray. The SBCC teams adequately prepare householders. The spray operator on reaching the house introduces himself with the Identification Card. With the permission of the householder, the spray operator together with the householder enters to inspect the rooms to be sprayed which are usually prepared as directed by the SBCC team. The operator then comes out to mix his insecticide, explaining every step to the householder after which he asks the householder to stay at a safe distance for spraying to be done in the rooms. Afterward, the spray operator reminds the householder to stay outside for a minimum of two hours. Household data, as recorded on the SP1 card, is submitted to the team leader who in turn collates and submits to the group supervisor. At the end of the day’s work, the spray operator returns to sprayed houses and does the final inspection of rooms to ensure the householder is satisfied with work done. The householder then signs the card. Communities earmarked for IRS are appropriately entered and prepared for at least three (3) days before spraying takes place.

Monitoring & Evaluation